Is Chikungunya Curable?
Understanding the Virus
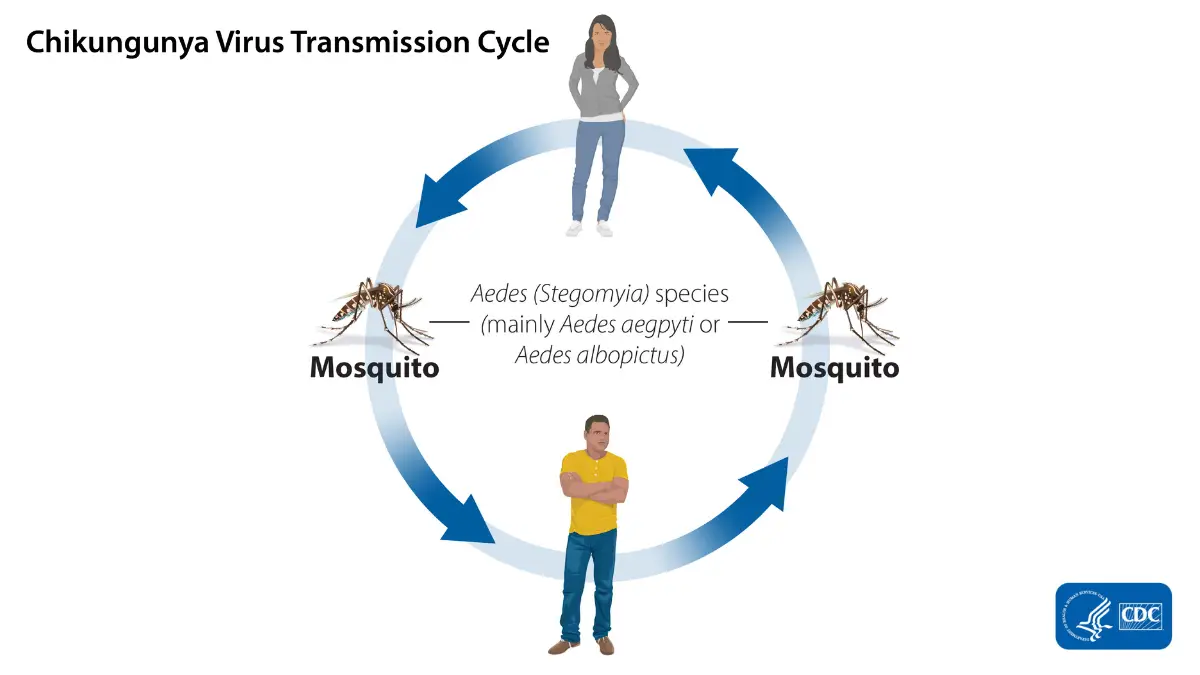
Chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes — mostly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. These are the same mosquitoes known for spreading Zika and dengue. First identified in Africa in the 1950s, chikungunya has since spread across many tropical and subtropical regions, including parts of Asia, the Americas, and the Caribbean.The word “chikungunya” comes from the Makonde language, meaning “to become contorted,” referencing the bent-over posture of people suffering from the intense joint pain the virus causes.
Is There a Cure for Chikungunya?
There is currently no specific cure for chikungunya.
Unlike bacterial infections that can be treated with antibiotics, chikungunya is caused by a virus. That means there’s no antiviral drug that can completely eliminate the virus from the body once someone is infected. However, this does not mean the situation is hopeless.
How Is Chikungunya Treated?
Although there’s no direct cure, chikungunya is a self-limiting illness, meaning most people recover on their own over time.
Supportive Care Includes:
- Rest: The body needs energy to fight off the virus.
- Hydration: Fever and sweating can lead to dehydration, so fluids are essential.
- Pain relief: Medications like paracetamol (acetaminophen) are commonly used to manage fever and joint pain. Avoid aspirin or NSAIDs until dengue is ruled out, as these can cause bleeding complications.
- Physical therapy: In cases where joint pain lingers, mild exercises and therapy may help ease stiffness and restore mobility.
How Long Does It Last?
- Acute phase: Symptoms such as fever and joint pain usually last between 5 to 10 days.
- Post-viral symptoms: For some people — especially older adults — joint pain may last for weeks or even months. This condition is called chronic chikungunya arthritis and can mimic symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Even though the virus may be gone from the body, the inflammation it triggered can persist in the joints.
Are There Any Long-Term Effects?
Most people recover fully, but in about 20–30% of cases, long-term joint pain can occur. This is more common in:
People over 50
- Those with pre-existing joint conditions
- Individuals who had a more severe initial infection
While this can be uncomfortable, it is not life-threatening and usually improves with time and treatment.
Is There a Vaccine?
As of now, no commercial chikungunya vaccine is available to the public, although several candidates are in clinical trials. Some progress has been made, and a few vaccines are close to approval in certain countries, but global access is still limited.
How to Prevent Chikungunya
Since there’s no cure, the best way to avoid chikungunya is to avoid mosquito bites. Here are a few preventive steps:
- Use insect repellent (like DEET or picaridin)
- Wear long-sleeved clothing
- Use mosquito nets and window screens
- Eliminate standing water near your home (mosquitoes breed in stagnant water)
Final Thoughts
To answer the original question — Is chikungunya curable?
Not in the traditional sense. There’s no pill or injection that clears the virus instantly. But with proper care, most people recover completely, even if it takes time. And for those who experience lingering symptoms, there are ways to manage the pain and regain strength gradually.As scientists continue to work on vaccines and antiviral treatments, public awareness and mosquito control remain our best defenses.






